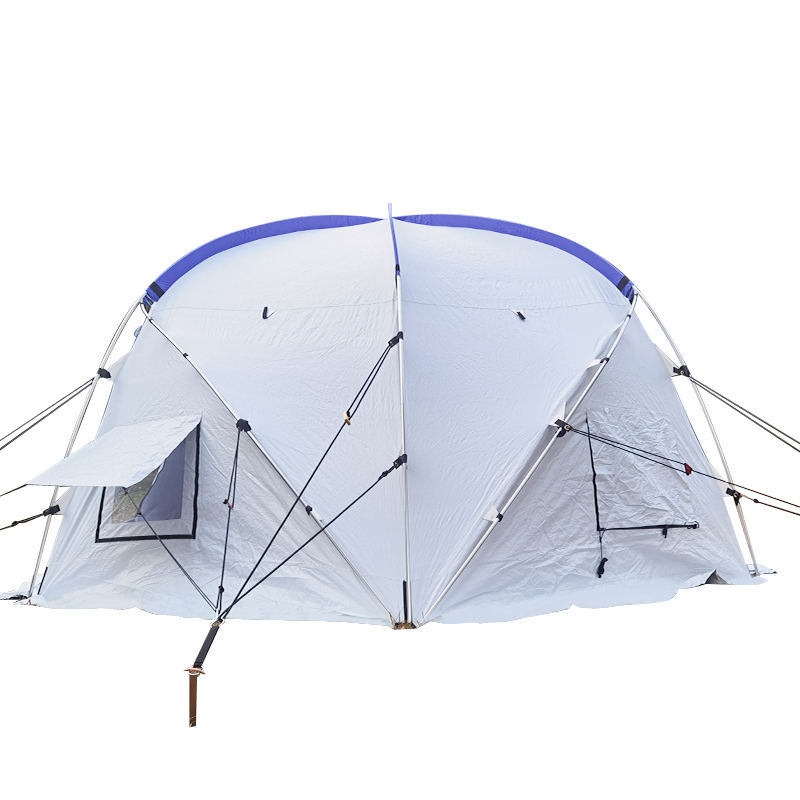
Our story is about how to uphold the spirit of humanitarianism in the face of disaster, how to find solutions amidst challenges, and how to sow hope in despair.
Web Menu
Product Search
Exit Menu
Storage Tents: The Secret Weapon for Unlocking Space Utilization
Posted by Admin | 17 Sep
Content
- 1 I. What is a Storage Tent? What are the Core Differences from Ordinary Tents?
- 2 II. What are the Common Types of Storage Tents? Which Scenarios are They Suitable For?
- 3 III. Core Advantages of Storage Tents: Why Can They Replace Some Traditional Warehousing Solutions?
- 3.1 1. Lower Cost: Significantly Reducing Initial and Long-term Costs
- 3.2 2. High Flexibility: Customizable and Easy to Relocate to Adapt to Dynamic Needs
- 3.3 3. Strong Adaptability: Coping with Complex Environments to Meet Diverse Scenario Needs
- 3.4 4. Higher Space Utilization: Column-free Design for Large Equipment and Bulk Storage
- 4 IV. Purchasing a Storage Tent: How to Avoid Pitfalls? Pay Attention to These 6 Points!
- 4.1 1. Clarify Your Needs: Avoid "Function Overkill" or "Insufficient Function"
- 4.2 2. Verify Materials and Craftsmanship: Control Quality from the Source
- 4.3 3. Confirm Technical Parameters: Reject "Vague Claims"
- 4.4 4. Focus on After-sales Service: Avoid "No Support After Purchase"
- 4.5 5. Calculate Comprehensive Costs: Avoid Being Misled by "Low Prices"
- 4.6 6. Check Actual Cases: Avoid "Paper Promises"
- 5 V. Using a Storage Tent: 6 Precautions for Safety and Efficiency
- 5.1 1. Site Preparation Before Assembly: Laying a Safe Foundation
- 5.2 2. Assemble Strictly According to the Instruction Manual: Avoid Operational Errors
- 5.3 3. Standardize Cargo Storage: Ensuring Safety and Efficiency
- 5.4 4. Cope with Severe Weather: Prevent Risks in Advance
- 5.5 5. Daily Inspection and Maintenance: Extending Service Life
- 5.6 6. Correct Disassembly and Storage: Preparing for Future Use
- 6 VI. Maintenance Tips for Storage Tents: How to Extend Service Life to Over 10 Years?
- 7 VII. Adaptation Solutions for Special Scenarios: How to Cope with Extreme Environments and Niche Needs?
- 8 VIII. Troubleshooting Common Storage Tent Issues: How to Resolve Problems Quickly?
- 8.1 1. Tarpaulin Water Seepage: Locate Leaks and Patch Targeted
- 8.2 2. Frame Noise: Mostly Due to Loose Connections or Uneven Stress
- 8.3 3. Rolling Door Jamming: Mostly Due to Track Debris or Insufficient Lubrication
- 8.4 4. Tarpaulin Bulging: Mostly Due to Insufficient Tension or Improper Fixing
- 8.5 5. Internal Humidity: Mostly Due to Poor Ventilation or Ground Moisture
- 8.6 6. Frame Rust: Address Early to Avoid Spread
- 9 IX. Comparison with Other Temporary Storage Facilities: How to Choose the Most Suitable One?
I. What is a Storage Tent? What are the Core Differences from Ordinary Tents?
By definition, a storage tent is a temporary or semi-permanent storage space that uses a modular frame (easily assembled and disassembled) as support and high-strength tarpaulin (with waterproof, sun-protective, and wear-resistant properties) as covering material. Its core purpose is to address space needs in scenarios such as cargo storage, equipment parking, and temporary operations. Its design standards must comply with relevant requirements in the "Technical Specifications for Temporary Storage Facilities," including structural stability, fire resistance rating, and environmental protection.
It has significant differences from ordinary camping tents, as detailed in the following comparison:
|
Comparison Dimension |
Storage Tent |
Ordinary Camping Tent |
|
Load-bearing Capacity and Stability |
Frame made of galvanized steel pipes/aluminum alloy, capable of withstanding 50-100kg/㎡ load and resisting winds up to level 11 (wind speed ≤30.6m/s) |
Frame made of fiberglass rods/light aluminum alloy, only bearing its own weight and resisting winds below level 5 (wind speed ≤10.7m/s) |
|
Space Scale |
Span ranging from 5 to 30 meters, extendable length (up to 100 meters for large models), usable area up to 2,000 square meters |
Span ranging from 1.5 to 3 meters, fixed length, usable area no more than 10 square meters |
|
Functional Adaptability |
Can be equipped with ventilation skylights (2-3 per 100㎡), rolling doors (3-5m wide), temperature control systems (0-15℃ adjustable), and moisture-proof mats (10mm thick); suitable for storing fresh produce, mechanical parts, and industrial raw materials |
Only has basic shelter function; no additional components, only suitable for storing personal items or providing temporary rest space |
|
Service Life |
5-10 years (5-6 years for basic models, 9-10 years for high-end models with regular maintenance) |
1-3 years (prone to tarpaulin aging and frame corrosion after 1 year of outdoor use) |
|
Application Scenarios |
Professional fields such as industry (raw material storage), agriculture (harvest season grain storage), logistics (peak season cargo preparation), and emergency response (disaster material transfer) |
Leisure scenarios such as outdoor camping, short-distance travel, and backyard gatherings |
Specifically, the frame of a storage tent is mostly made of galvanized steel pipes with a thickness of 2-4mm (hot-dip galvanized for rust resistance, zinc coating thickness ≥85μm) or 6061-T6 aluminum alloy (30% higher strength than ordinary aluminum alloy, lightweight for easy transportation). Some large-sized models also have reinforcing ribs installed at key joints (e.g., every 2 meters for arch-shaped tents) to withstand rain and snow loads—they can remain stable without snow removal when snow depth is ≤20cm, and no water leakage occurs during heavy rain (daily rainfall ≤150mm). In terms of space, it can be customized according to needs: a logistics park once built a 2,000-square-meter tent (100m long, 20m wide) to store 2,000 tons of goods, while ordinary camping tents can only accommodate 2-4 people and cannot meet cargo storage needs. In terms of functions, it can be tailored to goods characteristics: for fresh produce storage, a temperature control system can be added to maintain 0-10℃; for precision mechanical parts, a dust-proof net and moisture-proof layer (to control humidity at 40%-60%) can be installed—far exceeding the basic shelter function of ordinary camping tents.
II. What are the Common Types of Storage Tents? Which Scenarios are They Suitable For?
According to structural design, application scenarios, and functional requirements, storage tents can be divided into three main types, and the characteristics of different types determine their applicable scopes:
1. Container-type Storage Tents: Balancing Portability and Sealing
This type of tent is based on a standard container-sized frame (20-foot: 6.058m long, 2.438m wide; 40-foot: 12.192m long, 2.438m wide), compatible with container transportation standards. The frame is made of galvanized steel pipes with a thickness of 3mm, and the tarpaulin is PVC-coated mesh cloth (0.8-1.2mm thick, IPX7 waterproof rating—no water leakage when soaked in 1m deep water for 30 minutes, IP65 dust-proof rating—blocking 99% of dust). The tarpaulin and frame are fixed with sealing strips and snaps, ensuring excellent sealing performance.
Its core advantages are "portability + sealing": it can be folded for storage (folded volume is 1/5 of the expanded state; a 20-foot model can be transported by a 3-ton truck), and 2-3 people can assemble it within 2-4 hours without complex foundations (only flat ground is required). It is suitable for small to medium-sized cargo storage that requires a certain level of environmental protection.
Applicable Scenarios & Cases:
Outdoor construction equipment storage: In highway, railway, and other outdoor construction projects, engineering vehicles (e.g., excavators, loaders) need shelter at night or during rainy days. A railway project team moved and assembled container-type storage tents with the project progress—before using the tents, equipment corrosion rate was 25% due to open-air storage; after use, it dropped to below 5%, reducing equipment maintenance costs by nearly 200,000 yuan per year.
Emergency material transfer: During epidemics, natural disasters, and other emergencies, emergency materials (e.g., masks, medicines, food) need temporary storage and transfer. During an epidemic in a region in 2022, local rescue teams built 8 container-type storage tents as temporary material transfer stations within 3 hours, handling 100,000 pieces of materials daily and ensuring efficient material supply.
2. Large Arch-shaped Storage Tents: Unobstructed Space without Columns
Its core feature is a column-free span design (span usually 10-30 meters, maximum 40 meters). The frame is assembled from hot-dip galvanized steel pipes (zinc coating thickness ≥85μm, rust-resistant service life of more than 10 years) connected by bolts for strong structural stability. The tarpaulin is flame-retardant PVC material (complying with GB 8624-2012 Class B1 fire resistance standard: oxygen index ≥32%, self-extinguishing within 30 seconds after ignition, no molten drips, smoke toxicity reaching ZA1 level—non-toxic), fixed to the frame with ropes and snaps, and capable of resisting level 12 winds (wind speed ≤36.9m/s).
Due to the column-free design, the internal space is unobstructed (height 5-8 meters), convenient for the operation of large equipment such as forklifts and cranes (forklifts can turn and lift freely without avoiding columns). The usable area can reach 500-2,000 square meters or even larger, suitable for large-scale, heavy-duty storage scenarios such as industrial raw materials, large mechanical equipment, and bulk agricultural products.
Applicable Scenarios & Cases:
Industrial raw material storage: Raw materials in steel, building materials, and other industries (e.g., steel, cement, sand) are large in size, heavy in weight, and need to avoid moisture and corrosion. A steel enterprise built a large arch-shaped storage tent (30m span, 50m long) to store 5,000 tons of steel. Compared with open-air storage, the steel corrosion rate dropped from 30% to 5%, and forklift operation efficiency increased by 40%, reducing raw material loss costs by more than 300,000 yuan per year.
Large mechanical equipment storage: Large equipment in agriculture (combine harvesters, tractors) and engineering (road rollers, tower cranes) requires large storage space, and fixed warehouses have high construction costs. An agricultural cooperative used an arch-shaped tent (20m span, 30m long) to store 10 combine harvesters—the construction cost was only 1/3 of that of a fixed warehouse, and the time for equipment access was reduced from 2 hours to 30 minutes.
Bulk agricultural product storage: During the harvest season of grain, fruits, and vegetables, a large amount of space is needed for bulk storage. A grain-growing base used an arch-shaped tent (15m span, 40m long) to store 2,000 tons of wheat. Equipped with ventilation skylights and moisture-proof mats (10mm thick, no condensation when humidity ≤85%), the wheat mold rate dropped from 10% to below 1%, reducing grain loss by more than 18 tons per year.
3. Small Portable Storage Tents: Easy Assembly by One Person
It usually has a span of 3-8 meters and a length of 3-6 meters, with a usable area of 9-48 square meters. Even for models with an area of 9-10㎡ (overlapping with the maximum area of ordinary camping tents), the small portable storage tent differs significantly: its frame uses 1.5-2mm thick aluminum alloy (vs. 0.8-1mm fiberglass rods for camping tents), and the tarpaulin adopts IPX6 waterproof PVC (vs. IPX4 for most camping tents), making it suitable for storing small batches of goods (e.g., 50-100 boxes of snacks) rather than just personal items.The frame is made of lightweight aluminum alloy (1.5-2mm thick, lightweight—each frame rod weighs no more than 3kg) assembled with snap joints (no tools required, manual assembly possible). The tarpaulin is PVC-coated cloth (0.6-0.8mm thick, IPX6 waterproof rating—resistant to heavy rain, UPF50+ sun protection rating—blocking 98% of UV rays), which can be folded (folded volume is about 0.5 cubic meters, weight 10-30kg, portable by one person).
Its core advantages are "lightweight + quick assembly": one person can complete assembly within 1 hour according to the instruction manual (no professional skills required, fastest assembly from unpacking to completion takes only 40 minutes), and no complex site preparation is needed (flat ground such as yards, balconies, and store entrances is sufficient). It is suitable for scattered storage scenarios such as household sundries storage, small store temporary cargo storage, and outdoor stall temporary goods preparation.
Applicable Scenarios & Cases:
Household sundries storage: Seasonal items (e.g., winter down jackets, quilts; summer air conditioning quilts, fans) and gardening tools (e.g., hoes, shovels, flower pots) in families often take up a lot of indoor space. A family built a small tent (4m×3m) in the yard to store these items, freeing up 20 square meters of indoor space—after 2 years of storage, the items showed no signs of moisture or mold.
Small store temporary cargo storage: Small stores such as convenience stores and grocery stores often face insufficient warehouse space, especially during holidays. A convenience store built a small tent (5m×4m) at the store entrance to store temporary goods such as beverages and snacks—cargo preparation volume increased by 50%, and a transparent window was opened on the tent side for customers to select directly, increasing holiday sales by 25%.
Outdoor stall temporary goods preparation: Outdoor operators such as night market vendors and market traders need temporary storage for goods and to cope with sudden weather changes. A night market vendor used a small tent (3m×3m) to store goods during the day to avoid sun exposure, and extended the stall area with the tent at night—after use, business revenue increased by 30%, and cargo loss rate dropped from 15% to 2%.
III. Core Advantages of Storage Tents: Why Can They Replace Some Traditional Warehousing Solutions?
Compared with traditional fixed warehouses and open-air storage, storage tents have significant advantages in cost, flexibility, and adaptability, making them a preferred solution for many scenarios. The specific core advantages can be summarized into five points:
1. Lower Cost: Significantly Reducing Initial and Long-term Costs
The construction cost of traditional fixed warehouses is extremely high, including land approval, foundation construction, and main structure construction—about 1,000-2,000 yuan per square meter (a 1,000-square-meter warehouse has a total cost of 1-2 million yuan) with a construction period of 3-6 months. In contrast, storage tents do not require complex foundations (basic models only need flat ground; complex models need a simple concrete cushion with a cost of 20-50 yuan per square meter), and the main assembly cost is only 100-300 yuan per square meter (a 1,000-square-meter tent has a total cost of 100,000-300,000 yuan)—only 1/5-1/3 of that of fixed warehouses. Moreover, the assembly period is short (a 1,000-square-meter large tent can be assembled within 4-8 hours), allowing quick put-into-use and reducing waiting costs.
In terms of long-term use, storage tents have no property fees or fixed asset depreciation pressure (they can be disassembled and reused, with a service life of 5-10 years). If relocation is needed, they can be disassembled and reassembled at the new site without secondary investment. Fixed warehouses, however, are immovable—if the site is changed, previous investments will be completely wasted.
2. High Flexibility: Customizable and Easy to Relocate to Adapt to Dynamic Needs
The "modular design" of storage tents gives them strong flexibility: on one hand, the size can be customized according to needs—span can be adjusted from 5 meters to 40 meters, and length from 3 meters to 100 meters—allowing precise matching of space based on the volume and quantity of stored goods to avoid waste. On the other hand, they can be quickly disassembled and relocated: if an enterprise needs to change the storage location due to business adjustments (e.g., factory relocation, logistics site transfer), the tent can be disassembled, transported to the new site by truck, and reassembled for continued use—the relocation cost is only 10%-20% of the assembly cost (mainly labor and transportation fees).
In addition, the functions of storage tents can be flexibly expanded: heat insulation layers can be added according to seasonal changes (for cooling in summer and heat preservation in winter), temperature control equipment can be added according to goods characteristics (for fresh produce storage), and rolling doors can be added according to operation needs (for equipment access)—no large-scale renovation is required like fixed warehouses. For example, an agricultural product processing enterprise needed to store fresh fruits and vegetables (requiring 0-10℃ constant temperature) in summer and dried goods (requiring ventilation and moisture prevention) in winter. By adding detachable temperature control equipment and ventilation systems to the same tent, it achieved "one tent for two purposes"—no need to build separate cold storage and dried goods warehouses, reducing equipment investment by more than 50%.
3. Strong Adaptability: Coping with Complex Environments to Meet Diverse Scenario Needs
The structure and materials of storage tents are specially designed to adapt to the use needs of different regions and environments: in rainy areas, the tarpaulin has an IPX6-IPX7 waterproof rating and can resist typhoons up to level 11 (wind speed ≤32.6m/s); the frame base is fixed with expansion bolts or counterweights to prevent being blown down by strong winds. In high-temperature areas, the tarpaulin has sun-protective and heat-insulating properties (UPF50+, blocking 98% of UV rays, internal temperature 5-8℃ lower than the outside); ventilation skylights can be used to maintain internal coolness. In cold areas, heat insulation layers (50-100mm thick, thermal insulation performance equivalent to a 10cm thick brick wall) can be added, and heating equipment can be used to maintain an internal temperature above 5℃. In dusty, corrosive environments (e.g., mining areas, chemical parks), corrosion-resistant materials can be selected for the tarpaulin, and anti-corrosion coatings can be added to the frame to extend service life.
In contrast, open-air storage cannot resist severe weather at all, with a cargo loss rate as high as 10%-30%. Fixed warehouses can shelter from wind and rain but cannot adapt to site changes (e.g., outdoor construction, temporary disaster relief), and in extreme weather (e.g., strong typhoons), some old warehouses may suffer from roof collapse or wall water seepage. For example, a mining enterprise used corrosion-resistant storage tents to store equipment parts in a dusty, high-humidity mining area. The tents showed no obvious damage after 5 years of use, and the part loss rate dropped from 25% (open-air storage) to 3%. If a fixed warehouse had been built instead, the warehouse walls and roof would have required renovation every 3-5 years due to the harsh mining environment, with each renovation costing over 100,000 yuan.
4. Higher Space Utilization: Column-free Design for Large Equipment and Bulk Storage
Large arch-shaped storage tents adopt a "column-free span design," with no internal supporting columns, resulting in a space utilization rate of over 95% (traditional fixed warehouses have a utilization rate of 80%-85% due to columns and wall thickness). This design accommodates the operation of large equipment such as forklifts and cranes—forklifts can move, turn, and lift freely without avoiding columns. Goods can be stacked up to the top of the tent (5-8 meters high), significantly increasing storage density. For example, a building materials enterprise used an arch-shaped tent with a 20-meter span and 6-meter height to store cement and sand. The internal stacking height reached 5 meters, achieving a storage capacity of 1.2 tons per square meter. In contrast, traditional fixed warehouses, limited by column obstacles, only achieved 0.8 tons per square meter—representing a 50% increase in space utilization for the tent, and an additional 400 tons of goods stored in the same area.
In addition, storage tents can be flexibly adjusted in length and span according to the shape of the site. Even for irregular sites (e.g., triangular or polygonal areas), modular splicing can be used to adapt, avoiding space waste. Fixed warehouses, however, are limited by site shape and often require site cutting, resulting in idle space.
IV. Purchasing a Storage Tent: How to Avoid Pitfalls? Pay Attention to These 6 Points!
The quality of storage tent products on the market varies greatly, with prices ranging from several thousand yuan to several hundred thousand yuan. Blind purchasing may lead to problems such as "substandard quality, mismatched functions, or no after-sales support." Focus on the following 6 points to ensure you select a product that meets your needs:
1. Clarify Your Needs: Avoid "Function Overkill" or "Insufficient Function"
Before purchasing, clearly define four core needs to avoid blind selection:
Cargo Characteristics: If storing temperature- or humidity-sensitive goods (e.g., fresh produce, precision equipment), select models that can be equipped with temperature control and moisture-proof systems. For heavy goods (e.g., steel, sand), prioritize frames with a load-bearing capacity of at least 80kg/㎡.
Usage Scenario: For long-term outdoor use, select tents with a wind resistance rating of level 10 or above and UPF50+ sun protection. For temporary emergency use, prioritize portable models with quick assembly.
Site Conditions: For narrow sites, select models with a small span (5-10 meters) and adjustable length. For soft ground (e.g., soil, grass), confirm whether counterweights are required (to prevent frame tilting).
Usage Cycle: For short-term use (1-2 years), basic configuration models are sufficient. For long-term use (5+ years), focus on frame materials (hot-dip galvanized steel pipes preferred) and tarpaulin wear resistance (PVC mesh cloth with thickness ≥0.8mm recommended).
2. Verify Materials and Craftsmanship: Control Quality from the Source
Materials and craftsmanship directly determine the service life and safety of storage tents. Verify the following items one by one during purchasing:
Frame Materials: Prioritize hot-dip galvanized steel pipes (zinc coating thickness ≥85μm; test with a magnet—pure galvanized steel pipes are non-magnetic to avoid "cold galvanized" or ordinary iron pipe products, which rust within 1-2 years). For small portable models, 6061-T6 aluminum alloy is optional (high strength, lightweight; confirm cross-sectional thickness ≥1.5mm to avoid bending of thin aluminum pipes).
Tarpaulin Quality: Request a tarpaulin test report, focusing on waterproof rating (≥IPX6), flame retardancy (complying with GB 8624-2012 Class B1), and tear resistance (warp and weft directions ≥200N/5cm). Conduct on-site tests: spray water on the tarpaulin surface to check for seepage, and scratch the tarpaulin coating with your nails to check for peeling.
Connection Craftsmanship: Frame connections should use bolt fastening (avoid spot welding or snap connections—spot welding is prone to cracking, and snaps loosen after long-term use). The connection between the tarpaulin and frame should include sealing strips (to prevent water seepage from gaps), and the rope tensile strength should be ≥500N (to avoid breakage under strong winds).
3. Confirm Technical Parameters: Reject "Vague Claims"
Some merchants use vague descriptions such as "windproof and waterproof" or "durable" to mislead consumers. Request specific technical parameters and verify their authenticity:
Wind Resistance Rating: Clearly specify the maximum wind speed the tent can withstand (e.g., "resists level 12 wind, wind speed ≤32.7m/s"), rather than just "resists strong winds."
Load-bearing Capacity: Distinguish between "static load" (snow, stacked goods weight) and "dynamic load" (impact weight from forklift operations). For heavy goods storage, confirm the dynamic load capacity is ≥100kg/㎡.
Waterproof Performance: In addition to the waterproof rating, confirm that tarpaulin seams are heat-sealed (sealing width ≥5cm to avoid water seepage from stitched seams).
Environmental Indicators: For food or pharmaceutical storage, confirm the tarpaulin is odorless and complies with GB 4806.7-2016 (food contact material standard) to avoid harmful substance migration that could contaminate goods.
If a merchant cannot provide specific parameters or refuses to guarantee their authenticity, proceed with caution to avoid purchasing "three-no" (no brand, no standard, no certification) products.
4. Focus on After-sales Service: Avoid "No Support After Purchase"
Problems such as loose frames or torn tarpaulins may occur during use, making comprehensive after-sales service crucial:
Warranty Period: Clearly define the warranty scope and duration—frames should have a warranty of at least 3 years (free replacement for rust or cracking), and tarpaulins at least 1 year (free repair or replacement for water seepage or coating peeling due to non-human damage).
Maintenance Response: Confirm whether on-site maintenance services are provided (especially for large tents, which are difficult to repair independently) and the maintenance response time (24-hour on-site support for emergencies).
Accessory Supply: Inquire whether vulnerable parts (e.g., bolts, sealing strips, ropes) are available for long-term supply to avoid situations where tents cannot be repaired due to discontinued accessories 2-3 years after purchase.
5. Calculate Comprehensive Costs: Avoid Being Misled by "Low Prices"
Some merchants use "low prices" as a gimmick, but their products are "cut down" in quality. Calculate comprehensive costs rather than just the initial price:
Hidden Costs: Low-priced tents may require additional accessory purchases (e.g., counterweights, moisture-proof mats) or have a short service life (2-3 years, requiring replacement), making them more expensive in the long run. For example, a low-priced tent may cost 10,000 yuan less than a high-quality model initially, but with a service life of only 2 years (vs. 8 years for the high-quality model), the annual average cost is higher.
Installation Costs: Confirm whether the quotation includes installation services. For large tents, self-hiring installation teams may cost an additional 5,000-20,000 yuan.
Disassembly Costs: If relocation is needed in the future, confirm whether disassembly guidance or services are provided to avoid tent damage due to improper disassembly (resulting in greater losses from repurchasing).
It is recommended to list the total cost of "initial purchase + accessories + installation + maintenance" and compare products to select the one with the highest cost-effectiveness.
6. Check Actual Cases: Avoid "Paper Promises"
Request the merchant to provide actual use cases of the same type of product (e.g., applications in the same industry or similar scenarios). Whenever possible, conduct on-site inspections or contact users to understand their experience:
Inspection Focus: The tent’s actual stability (e.g., whether it has withstood heavy rain or strong winds), cargo storage effects (e.g., whether moisture or loss occurred), and after-sales response speed.
Avoid "Rendering Traps": Some merchants display computer-rendered images—request actual photos or videos of the installed tent to confirm consistency with promotions.
V. Using a Storage Tent: 6 Precautions for Safety and Efficiency
Even with a high-quality storage tent, improper use can lead to safety hazards or shortened service life. Follow these 6 precautions:
1. Site Preparation Before Assembly: Laying a Safe Foundation
Site preparation directly affects tent stability. Complete three key tasks:
Site Leveling: Remove stones, weeds, and protrusions from the site. Use a level to confirm the ground slope is ≤3° (slopes exceeding this can cause frame tilting or collapse). For soft ground (e.g., soil), lay a gravel cushion (thickness ≥10cm) or install ground beams (to enhance load-bearing).
Drainage Planning: Dig drainage ditches (width ≥30cm, depth ≥20cm) around the tent to prevent rainwater accumulation from soaking the tent base (causing frame rust or tarpaulin mold). In rainy areas, raise the tent base by 10-15cm (using bricks or concrete blocks).
Surrounding Environment: Ensure the tent is at least 5 meters away from high-voltage lines (to avoid electric shock risks), 3 meters away from tall trees (to prevent branch damage during strong winds), and 10 meters away from flammable materials (e.g., gasoline, diesel). Even with flame-retardant tarpaulins, external fire sources must be avoided.
2. Assemble Strictly According to the Instruction Manual: Avoid Operational Errors
Follow the product manual strictly during assembly—do not rely on experience. Focus on:
Component Installation Sequence: Follow the order of "foundation fixing → frame assembly → tarpaulin covering → accessory installation." Avoid reversing steps (e.g., covering the tarpaulin before frame assembly, which can tear the tarpaulin).
Bolt Tightening: Use a torque wrench to tighten all frame bolts to the specified torque (usually 30-50N·m, refer to the manual). Avoid over-loosening (causing frame shaking) or over-tightening (breaking bolts). After assembly, check each bolt one by one, and re-tighten after 24 hours (frame slight loosening may occur under stress).
Tarpaulin Installation: Avoid dragging the tarpaulin during covering (to prevent scratches from sharp objects on the ground). Pull the tarpaulin tight and flat (to avoid water accumulation—excess weight from accumulated water can collapse the frame). Align the tarpaulin seams with the sealing strips to ensure no gaps.
3. Standardize Cargo Storage: Ensuring Safety and Efficiency
Reasonable cargo storage prevents tent overloading and damage. Follow these rules:
Weight Distribution: Stack goods evenly to avoid one-sided overloading (e.g., stacking heavy goods only on one side of the tent, which can bend the frame). The stacking height should not exceed 80% of the tent’s internal height (to reserve ventilation space and prevent goods from touching the tarpaulin, which could tear it).
Classified Storage: Store goods of different characteristics separately—place damp goods (e.g., fresh produce) in well-ventilated areas and elevate them with pallets (≥10cm, to prevent ground moisture seepage). Isolate flammable goods (e.g., paint, alcohol) separately, prohibit open flames inside the tent, and equip dry powder fire extinguishers (at least 1 per 50 square meters).
Passage Reservation: Reserve passages ≥1.5 meters wide inside the tent (to facilitate forklift operations and personnel evacuation). Do not stack goods on both sides of passages (to avoid blocking escape routes).
4. Cope with Severe Weather: Prevent Risks in Advance
Take preventive measures for severe weather such as heavy rain, strong winds, or snow:
Strong Winds: Before wind speeds exceed the tent’s resistance rating (e.g., reinforce for winds above level 8 if the tent resists level 10), close all doors and windows, tighten tarpaulin ropes, and reinforce the frame base (add counterweights, ≥50kg per square meter). For tents in open areas, build windbreaks around them (e.g., using color steel plates or sandbags, height ≥2 meters).
Heavy Rains: Clean drainage ditches in advance, check for tarpaulin damage (repair small holes promptly to avoid expanding leaks), place water-receiving containers inside the tent (to handle sudden seepage), and elevate goods to prevent rainwater backflow.
Snowfall: Remove snow promptly when the depth exceeds 20cm (use soft tools such as plastic shovels to avoid scratching the tarpaulin). Clear snow from the sides to the center to prevent accumulation on the top (increasing load). If snow is too thick, temporarily remove some goods to reduce tent load.
5. Daily Inspection and Maintenance: Extending Service Life
Regular inspections can identify problems early, preventing minor faults from becoming major damage. Establish a "daily + weekly + monthly" inspection system:
Daily Inspection (1x per day): Check for tarpaulin damage, frame abnormal noises, or ground water accumulation.
Weekly Inspection (1x per week): Tighten loose bolts, clean dust and debris from the tarpaulin surface (to avoid affecting sun protection and breathability), and check for blocked drainage ditches.
Monthly Inspection (1x per month): Check the frame for rust (paint rusted areas promptly), verify that sealing strips at tarpaulin seams are not falling off (reapply if needed), and ensure accessories (e.g., rolling doors, ventilation skylights) operate normally.
6. Correct Disassembly and Storage: Preparing for Future Use
When the tent is not in use for a long time or needs to be relocated, proper disassembly and storage are essential to avoid damage:
Disassembly Sequence: Follow the order of "accessory removal → tarpaulin removal → frame disassembly." Avoid violent disassembly (e.g., hitting frame joints with a hammer, which can cause deformation). For rolling doors or ventilation skylights, first remove electrical components (if equipped) to prevent wire damage.
Tarpaulin Handling: After removing the tarpaulin, clean it thoroughly with a neutral detergent (avoid strong acids or alkalis that damage the coating), rinse with clean water, and dry completely (moisture can cause mold during folding). When folding, place newspaper between layers to absorb residual moisture and prevent coating adhesion.
Frame Handling: After disassembling the frame, wipe off surface dust and rust with a dry cloth. For rust spots, sand them down and apply anti-rust paint (one coat of primer + two coats of topcoat). Classify small parts such as bolts and snaps into sealed bags, label them clearly (e.g., "frame corner bolts"), and store them with the frame to avoid loss.
Storage Environment: Store all components in a dry, well-ventilated indoor space (temperature 0-30℃, humidity ≤60%). Avoid outdoor storage (sunlight and rain accelerate aging) and keep them away from corrosive substances (e.g., chemical fertilizers, pesticides). For long-term storage (over 6 months), inspect the tarpaulin and frame every 2 months to prevent mold or rust.
VI. Maintenance Tips for Storage Tents: How to Extend Service Life to Over 10 Years?
Proper maintenance not only ensures the tent’s safety but also extends its service life from 5 years to over 10 years, reducing long-term costs. The core maintenance tips include three aspects:
1. Special Maintenance for Tarpaulins: Preventing Aging and Damage
The tarpaulin is the "protective layer" of the tent, so focused maintenance is critical:
Cleaning Frequency: Clean the tarpaulin once a month for outdoor use, and every 2 weeks in dusty environments. Use a soft-bristle brush dipped in neutral detergent to gently scrub (avoid hard brushes that scratch the coating), then rinse with clean water. Never use a high-pressure water gun (excessive pressure damages the waterproof coating).
Damage Repair: For small damages (diameter ≤5cm), use special tarpaulin tape (matching the tarpaulin material) for patching. Before patching, clean the damaged area with alcohol to remove dust and oil, then press firmly for 5 minutes to ensure adhesion. For damages over 10cm², contact professionals to replace a local section of the tarpaulin (avoid the higher cost of full replacement).
Anti-aging Measures: Apply a special anti-aging agent to the tarpaulin surface every spring and autumn (extending the coating’s life by 2-3 years). In hot summers, install a sunshade net on top of the tent to reduce UV radiation and slow aging. During long-term winter idleness, ventilate the storage space once a month to prevent mold growth.
2. Regular Maintenance for Frames: Preventing Rust and Deformation
The frame is the "skeleton" of the tent, with maintenance focused on rust prevention and deformation correction:
Rust Prevention: Conduct a comprehensive inspection of the frame before the rainy season each year. For rust spots (especially at joints), sand them down to expose the metal surface, then apply anti-rust primer (1 coat) and topcoat (2 coats), ensuring an even coating (thickness ≥50μm). In coastal areas (high salt spray environments), perform rust prevention once every 6 months.
Deformation Correction: For slight frame bending (e.g., crossbar bending ≤5cm), contact professionals to correct it with hydraulic tools (avoid manual brute-force correction, which can cause fractures). For severe bending, replace the frame component to prevent overall structural instability.
Connection Maintenance: Inspect bolts and connectors at frame joints quarterly. Replace worn or deformed parts promptly (bolts should be fully replaced every 2 years to avoid aging and breakage). Apply grease to connectors every 6 months to reduce friction and wear.
3. Accessory Maintenance: Ensuring Normal Functionality
The normal operation of accessories such as rolling doors, ventilation skylights, and temperature control equipment directly affects the tent’s usability. Maintain each accessory as follows:
Rolling Doors: Clean dust and debris from the track weekly to avoid jamming. Apply lithium-based lubricant to the track and reel monthly (choose low-temperature-resistant lubricant to prevent freezing in winter). Check the rolling door motor (if equipped) for loose wiring to avoid short circuits.
Ventilation Skylights: Inspect the hinges and latches of skylights monthly to ensure flexible opening and closing. Apply anti-rust oil to hinges every quarter. Clean the skylight filter (if equipped) to prevent dust blockage and maintain ventilation efficiency.
Temperature Control Equipment: For tents with air conditioning or heating devices, clean the filter and inspect the wiring regularly according to the equipment manual. Have a professional conduct a full inspection annually to avoid cargo damage caused by equipment failure.
VII. Adaptation Solutions for Special Scenarios: How to Cope with Extreme Environments and Niche Needs?
Beyond conventional industrial and agricultural scenarios, storage tents can also be used in extreme environments (e.g., alpine regions, coastal salt spray areas) and for niche needs (e.g., food-grade storage, explosion-proof storage). However, targeted configuration adjustments are required. The following table summarizes the core configurations for four special scenarios:
|
Scenario Type |
Core Material Requirements |
Key Structural Reinforcement |
Essential Functional Configurations |
Example Applicable Goods |
|
Alpine and High-Altitude ( -30℃ to 0℃, altitude ≥3000m) |
Frame: Low-temperature-resistant galvanized steel pipes (with nickel, 20% higher tensile strength); Tarpaulin: Cold-resistant PVC mesh cloth (brittleness temperature ≤-40℃) |
Add 1 horizontal reinforcing rib every 2 meters; Use precast concrete blocks for weighting (≥80kg/㎡) at the base |
Double-layer insulated tarpaulin (50mm rock wool inner layer); Fuel-fired heaters (with oxygen deficiency protection); UV-resistant coating |
Highland barley, yak feed, plateau agricultural products |
|
Coastal Salt Spray (salt spray concentration ≥0.05mg/m³) |
Frame: Hot-dip galvanized + passivated steel pipes (zinc coating ≥120μm, with fluorocarbon paint); Connectors: 316 stainless steel; Tarpaulin: Salt spray-resistant PVC |
Elevate the tent base by 30cm (using brick platforms); Dig salt spray diversion ditches (30cm wide, 20cm deep) around the tent |
Salt spray-resistant coating on tarpaulin surface; Regular fresh water flushing ports; Frame corrosion monitoring components |
Fishing nets, fishing gear, port machinery parts |
|
Food-Grade Storage (complying with GB 4806.7-2016) |
Frame inner side: Food-grade epoxy resin coating; Tarpaulin: Food-grade PVC (no plasticizer migration); Floor mat: Food-grade antibacterial material |
No sharp edges (to avoid damaging cargo packaging); Ground flatness error ≤3mm (to prevent floor mat damage) |
Food-grade moisture-proof floor mats (15mm thick, antibacterial rate ≥99%); UV disinfection lamps (2 per 100㎡); 3 air changes per hour ventilation system |
Rice, flour, edible oil, pre-prepared food ingredients |
|
Explosion-Proof Storage (flammable and explosive goods) |
Frame: Antistatic-treated steel pipes; Tarpaulin: Antistatic PVC (surface resistance ≤10⁸Ω); Connectors: Copper (spark-free) |
Frame grounding (ground resistance ≤4Ω); Explosion-proof isolation zones (5m wide) in cargo stacking areas |
Explosion-proof ventilation skylights (aluminum alloy, spark-free design); Explosion-proof lamps/switches (Ex d IIB T4Gb); 4kg dry powder fire extinguishers (2 per 50㎡) |
Paint, thinners, lithium batteries |
Practical Cases for Special Scenarios:
Alpine Regions: A herding cooperative on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau used alpine-adapted storage tents to store yak feed. Even at -25℃, the internal temperature remained above 0℃, and the feed showed no freezing or mold. Compared with open-air storage, the feed loss rate dropped from 30% to 5%.
Coastal Areas: A coastal fishing village used salt spray-resistant tents to store fishing nets. After 8 years of use, the frame showed no obvious rust, and the fishing nets remained intact without corrosion—saving 10,000 yuan annually in net replacement costs.
Food Industry: A food processing factory used food-grade storage tents to store pre-prepared vegetable ingredients. Over a 6-month storage period, the ingredients had no mold or odor, fully complying with national food safety testing standards.
Chemical Industry: A chemical enterprise used explosion-proof tents to store paint thinners. For 3 years, no safety accidents occurred, meeting the safety supervision requirements for flammable goods storage.
VIII. Troubleshooting Common Storage Tent Issues: How to Resolve Problems Quickly?
During use, tents may experience issues such as tarpaulin water seepage, frame noise, or rolling door jamming. Mastering basic troubleshooting methods can prevent minor problems from escalating into major failures. Here are solutions for 6 common issues:
1. Tarpaulin Water Seepage: Locate Leaks and Patch Targeted
Inspection Steps: After rain, observe the water seepage location inside the tent, then check the corresponding external tarpaulin for damage, missing sealing strips at seams, or gaps around ventilation skylights/rolling doors.
Solutions:
Small damages (≤5cm): Use special tarpaulin tape (matching the tarpaulin material) for
patching. Clean the leak area with alcohol, dry it, and press firmly for 5 minutes to
ensure adhesion.
Seam seepage: Reapply special tarpaulin sealant (thickness ≥2mm). After the sealant
dries, test with water (spray and observe for 24 hours to ensure no seepage).
Skylight/rolling door gaps: Install EPDM rubber sealing strips (10mm thick) and press
firmly to block water ingress.
2. Frame Noise: Mostly Due to Loose Connections or Uneven Stress
Inspection Steps: When noise occurs, check if frame bolts are loose, reinforcing ribs are deformed, or base weights are displaced.
Solutions:
Loose bolts: Retighten them with a torque wrench according to the manual’s specified
torque (usually 30-50N·m). Replace severely worn bolts to avoid slipping.
Deformed reinforcing ribs: For slight deformation (≤3cm), use a hydraulic jack to slowly
correct it (place a wooden board between the jack and frame to avoid damage).
Replace severely deformed ribs.
Displaced weights: Readjust the weight positions to ensure even distribution around the
tent. Add 20kg/m² of additional weight for soft ground.
3. Rolling Door Jamming: Mostly Due to Track Debris or Insufficient Lubrication
Inspection Steps: Observe where the rolling door jams, and check if the track contains stones or dust, or if the reel is rusted.
Solutions:
Track debris: Clean the track with a vacuum cleaner, then wipe the inner wall with a dry
cloth.
Insufficient lubrication: Apply lithium-based grease to the track and reel (avoid engine oil,
which attracts dust).
Rusted reel: Sand the rusted area, apply anti-rust paint, and lubricate after drying.
4. Tarpaulin Bulging: Mostly Due to Insufficient Tension or Improper Fixing
Inspection Steps: Observe the bulging area and check if tarpaulin ropes are loose or tarpaulin-frame connection snaps are missing.
Solutions:
Loose ropes: Retighten the tarpaulin ropes evenly from the tent’s perimeter to the center
(avoid over-tightening one side, which can deform the tarpaulin). Secure the rope ends
with turnbuckles for easy future adjustments.
Missing snaps: Reinstall snaps (ensuring a spacing of ≤50cm between each snap). If
the tarpaulin is worn at the snap location, reinforce it with tape before reinstalling.
5. Internal Humidity: Mostly Due to Poor Ventilation or Ground Moisture
Inspection Steps: Use a hygrometer to measure the internal humidity (normal humidity ≤60%). If humidity exceeds the standard, check if ventilation skylights are open, moisture-proof mats are damaged, or the ground has standing water.
Solutions:
Poor ventilation: Open the ventilation skylights for 2-3 hours daily (at 10:00 AM and 3:00
PM, avoiding low-temperature periods in the morning and evening). Install industrial
exhaust fans (1 per 100㎡) for high humidity.
Damaged moisture-proof mats: Replace the damaged mats and seal the seams with
tape.
Ground moisture: Lay a layer of plastic film (0.1mm thick) under the moisture-proof mat
to block ground moisture.
6. Frame Rust: Address Early to Avoid Spread
Inspection Steps: Regularly check the frame joints and base for red rust spots—address them promptly.
Solutions:
Slight rust (area ≤10cm²): Sand the rusted area to expose the metal surface, then apply
anti-rust primer (1 coat) and topcoat (2 coats).
Moderate rust (area 10-50cm²): In addition to sanding and painting, install stainless
steel reinforcement plates (3mm thick) on the rusted area to enhance frame strength.
Severe rust (area >50cm²): Replace the rusted frame component to avoid overall
structural risks.
IX. Comparison with Other Temporary Storage Facilities: How to Choose the Most Suitable One?
In addition to storage tents, temporary storage options include prefabricated houses, container warehouses, and inflatable warehouses. The characteristics of these facilities vary significantly, so selection should be based on specific needs. The following table compares their core parameters and applicable scenarios:
|
Comparison Dimension |
Storage Tents |
Prefabricated House Warehouses |
Container Warehouses |
Inflatable Warehouses |
|
Assembly Period |
Small models: 40 minutes - 2 hours; Large models: 4 - 8 hours (2 - 6 people operable) |
3 - 7 days (requires professional construction team for wall assembly, roof laying, and water/electricity connection) |
1 - 2 days (needs 12-ton+ crane for hoisting and positioning, 2 - 3 people coordinating) |
Small models: 30 minutes (with electric air pump); Large models: 2 - 4 hours (multiple air pumps needed) |
|
Mobility |
Detachable, components can be classified and packed; 1 3-ton truck can transport 100㎡ components; relocation cost: 200 - 300 yuan/㎡ |
Detachable but components are scattered (walls, roof, doors/windows need separate transportation); 100㎡ requires 3 - 5 trucks; relocation cost: 500 - 800 yuan/㎡ |
Integral hoisting, convenient for short-distance movement (within 10km); 20-foot container movement cost: ~1,000 yuan/unit; long-distance transportation needs logistics vehicles |
Foldable, folded volume is 1/10 of expanded state; 1 3-ton truck can transport 200㎡ components; relocation cost: 150 - 200 yuan/㎡ (note: avoid pressure on tarpaulin during transportation) |
|
Space Utilization |
Column-free design, utilization rate ≥95%; internal height 5 - 8 meters, adjustable according to span; goods can be stacked up to 80% of internal height |
With load-bearing columns (spacing 3 - 5 meters) and thick walls; utilization rate 80% - 85%; internal height usually 3 - 4 meters (limited by prefabricated board structure) |
Fixed size (20-foot: 6.058m×2.438m×2.591m; 40-foot: 12.192m×2.438m×2.591m); utilization rate 85%; internal height fixed, unable to adjust |
Column-free design, utilization rate ≥95%; internal height 3 - 5 meters (limited by air pressure); goods stacking height ≤70% of internal height (to avoid damaging the top tarpaulin) |
|
Wind Resistance |
Basic models: resist level 10 wind (wind speed ≤28.4m/s); Enhanced models: resist level 12 wind (wind speed ≤36.9m/s) |
Basic models: resist level 8 wind (wind speed ≤20.7m/s); Enhanced models (with wind-resistant columns): resist level 10 wind; walls are prone to being lifted by strong winds |
New containers: resist level 12+ wind (sturdy steel structure); Used containers (after anti-rust treatment): resist level 11 - 12 wind; suitable for coastal typhoon-prone areas |
Basic models: resist level 8 wind (wind speed ≤20.7m/s); Enhanced models: resist level 10 wind; tarpaulin is prone to tearing in gusts |
|
Cost per Square Meter |
Basic models (no additional functions): 100 - 150 yuan; Mid-range models (with ventilation/moisture-proof): 150 - 250 yuan; High-end models (with temperature control/explosion-proof): 250 - 300 yuan |
Basic models (only frame + walls): 300 - 350 yuan; Mid-range models (with doors/windows + water/electricity): 350 - 450 yuan; High-end models (with insulation layer + ceiling): 450 - 500 yuan |
New containers (modified with ventilation/moisture-proof): 800 - 1,200 yuan; Used containers (after rust removal + modification): 500 - 700 yuan (note: check for container deformation before purchase) |
Basic models (only tarpaulin + air frame): 80 - 120 yuan; Mid-range models (with basic ventilation/lighting): 120 - 180 yuan; High-end models (with moisture-proof + anti-aging coating): 180 - 200 yuan |
|
Service Life |
Basic models: 5 - 6 years; Mid-range models: 7 - 8 years; High-end models (with regular maintenance): 9 - 10 years |
Basic models (ordinary color steel plates): 8 - 10 years (prone to moisture and mold); Mid-range models (with anti-corrosion treatment): 10 - 12 years; High-end models (high-quality color steel + insulation layer): 12 - 15 years |
New containers: 15 - 20 years (steel structure is corrosion-resistant); Used containers: 8 - 12 years (requires annual rust removal and painting) |
Basic models (ordinary tarpaulin): 2 - 3 years; Mid-range models (anti-aging tarpaulin): 3 - 4 years; High-end models (reinforced airbag + anti-aging coating): 4 - 5 years |
|
Applicable Scenarios |
1. E-commerce peak season temporary cargo preparation (3 - 6 months); 2. Outdoor engineering equipment storage (1 - 2 years, movable with project); 3. Agricultural harvest season grain/fruit storage (3 - 6 months); 4. Medium-term emergency material transfer (6 - 12 months after disasters) |
1. Long-term construction site material warehouses (2 - 5 years, fixed storage); 2. Northern winter agricultural product insulation storage (needs 5 - 10℃, 3 - 4 months); 3. Remote area integrated office + storage (long-term fixed, needs water/electricity) |
1. Port heavy equipment parts storage (long-term fixed, typhoon-resistant); 2. Chemical raw material short-distance transfer storage (factory to wharf, corrosion-resistant); 3. Long-term fixed storage of heavy goods (steel/mechanical parts, load-bearing ≥100kg/㎡) |
1. Ultra-short-term emergency storage (7 - 15 days after earthquakes/floods); 2. Exhibition/event temporary cargo preparation (1 - 2 weeks for auto shows/music festivals); 3. Small farmers' short-term fruit/vegetable turnover (1 - 2 months after picking) |
Three-Step Selection Guide: Quickly Lock in the Suitable Solution
Step 1: Clarify "Usage Cycle + Mobility Needs"
If the usage cycle is ≤1 year and frequent relocation is required (e.g., 1 relocation within 3 months): Prioritize inflatable warehouses (lowest relocation cost) or small storage tents (suitable for scattered storage).
If the usage cycle is 1-3 years and 1-2 relocations are needed (e.g., 2-year construction period, requiring movement with the project): Prioritize storage tents (mid-range configuration, balancing cost and stability).
If the usage cycle is ≥3 years and no relocation is needed (e.g., long-term material warehouses for construction sites): Choose prefabricated house warehouses (mid-to-high-end configuration with insulation and moisture resistance) or container warehouses (modified used containers for lower cost).
Step 2: Evaluate "Cargo Characteristics + Environmental Requirements"
For storing fresh produce or precision equipment (needing temperature and humidity control: 0-15℃ temperature, 40%-60% humidity): Choose high-end storage tents (equipped with temperature control + moisture-proof systems) or mid-to-high-end prefabricated house warehouses (with insulation layers + air conditioners). Avoid inflatable warehouses (weak temperature and humidity control capabilities).
For storing heavy goods (e.g., steel, sand, needing load-bearing ≥80kg/㎡): Choose storage tents (reinforced frames) or container warehouses. Avoid prefabricated house warehouses (limited internal height and load-bearing capacity).
For extreme environments such as coastal areas or plateaus: Choose container warehouses (corrosion-resistant) or storage tents (enhanced salt spray-resistant models) for coastal areas; choose storage tents (alpine models, low-temperature resistant) for plateaus. Avoid inflatable warehouses (weak resistance to extreme environments).
Step 3: Calculate "Comprehensive Costs" (Avoid Focusing Only on Initial Price)
Short-term use (≤1 year): Comprehensive cost = initial purchase cost + relocation cost (if any). Inflatable warehouses are the most cost-effective (e.g., 100㎡ costs 12,000 yuan, saving 8,000 yuan compared to storage tents).
Mid-term use (1-3 years): Comprehensive cost = initial purchase cost + 1-2 relocation costs + annual maintenance cost. Mid-range storage tents are better (e.g., 100㎡ initial cost 20,000 yuan, 2 relocations cost 4,000 yuan, annual maintenance cost 2,000 yuan; total 26,000 yuan over 3 years, saving 32,000 yuan compared to prefabricated house warehouses).
Long-term use (≥3 years): Comprehensive cost = initial purchase cost + 0-1 relocation cost + 3-year maintenance cost. Mid-to-high-end prefabricated house warehouses or modified used container warehouses are more cost-effective (e.g., 100㎡ prefabricated house initial cost 40,000 yuan, 3-year maintenance cost 6,000 yuan; total 46,000 yuan, saving 20,000 yuan compared to high-end storage tents over 5 years).
Conclusion: Storage Tents—A Practical and Reliable Choice for Space Shortages
When logistics parks face peak-season cargo overstock, when farmers need to protect harvests from mold and corrosion, when construction teams require mobile shelters for engineering equipment, or when rescue teams race to set up temporary material transfer stations after disasters, storage tents consistently prove their irreplaceable value. They are not just "temporary covers" but well-designed solutions that balance cost, flexibility, and functionality.
Compared with traditional fixed warehouses, storage tents eliminate the burden of high construction costs and long approval cycles, allowing users to put storage space into use in hours rather than months. Unlike open-air storage, their sturdy frames and high-performance tarpaulins shield goods from wind, rain, snow, and dust, slashing cargo loss rates from 10%-30% to below 5%. Even when pitted against other temporary facilities like prefabricated houses or inflatable warehouses, storage tents stand out for their combination of portability (relocation costs only 10%-20% of assembly costs), high space utilization (over 95% with column-free designs), and adaptability (customizable for alpine, coastal, food-grade, or explosion-proof scenarios).
For any user grappling with space constraints—whether a small convenience store owner needing extra holiday storage, a large steel enterprise storing raw materials, or a rescue team responding to emergencies—storage tents offer a "right-fit" answer. They do not rely on grand technological promises but on down-to-earth performance: durable materials that last 5-10 years, easy assembly that requires no professional skills, and maintenance routines that extend service life without heavy effort.
In the end, the true strength of storage tents lies in their ability to turn "space shortages" into "space solutions"—simply, efficiently, and reliably. For anyone seeking to unlock space potential without compromising on cost or safety, storage tents are more than a choice; they are a proven, practical asset.
Related Products
- Cell Phone:+86 15695147631
- Cell Phone:+86 18630605111
-
Email:
[email protected]
[email protected]
[email protected] - Add:No.9 Kangmin Road, Automobile industry Park, Yizheng City, Jiangsu Province, China
Copyright © Yangzhou Mailenda Outdoor Products Co., Ltd.
All Rights Reserved.
Custom Tent OEM/ODM Manufacturers

- Privacy Statement
- Terms & Conditions
- Sitemap


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 Español
Español 日本語
日本語 русский
русский عربى
عربى