Our story is about how to uphold the spirit of humanitarianism in the face of disaster, how to find solutions amidst challenges, and how to sow hope in despair.
Web Menu
Product Search
Exit Menu
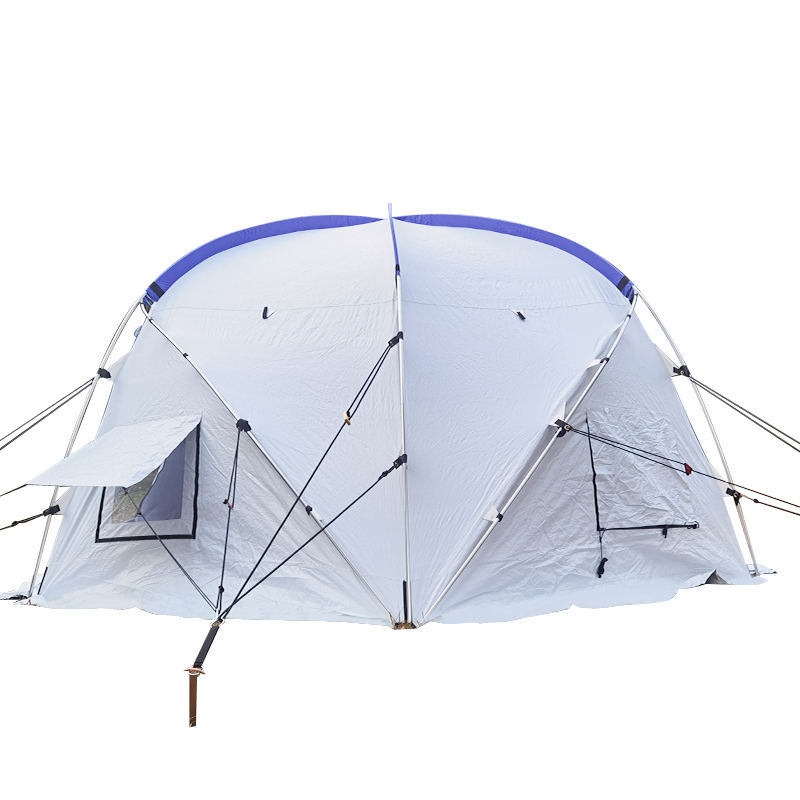
How do Inflatable Tents perform in extreme weather conditions?
Posted by Admin | 19 Dec
Content
Performance of Inflatable Tents in Extreme Weather Conditions
1. Structural Integrity and Air Pressure Balance
Air Pressure Maintenance: The core of an inflatable tent is maintaining constant internal air pressure. Extreme high temperatures can cause excessive gas expansion, while low temperatures can cause gas contraction, resulting in air pressure below the design standard, directly affecting structural stability.
Tear Resistance: Facing extremely strong wind pressure, the tear resistance of the inflatable beam material (such as PVC or TPU) is crucial. If the material is not thick enough or is aged, it will not be able to withstand the damage caused by instantaneous wind pressure.
2. Wind Load and Shape Adaptability
Flexible cushioning advantage: Compared with steel brackets, inflatable beams have a certain degree of flexibility. This flexibility can absorb wind energy, preventing direct breakage due to uneven stress on rigid structures, thus preventing "overturning" to a certain extent.
Wind direction pressure points: In extreme weather, the wind impact surface must be minimized. The streamlined design of inflatable tents helps reduce wind resistance, but if the internal structure is excessively flattened, it may cause external wind to directly rush into the air inlet or other weak points.
3. Waterproofing and Drainage System
Water sealing: Water pressure during heavy rain is another major test for tents. Inflatable tents are usually equipped with high-quality waterproof layers and sealed seams (such as heat sealing technology), which can effectively prevent rainwater penetration, preventing slippery internal floors or damp equipment.
Drainage design: The drainage grooves or angled design of the canopy directly determine the efficiency of rainwater drainage. If the drainage system is poorly designed, rainwater may accumulate inside the tent, increasing the structural load.
4. Emergency Response Mechanism
Rapid evacuation and reinforcement: When extreme weather arrives, the advantage of inflatable tents is that they can be "dismantled at any time." If the wind is extremely strong, the ability to quickly evacuate and reinforce is more crucial than simply resisting the wind.
Over-inflation risk: If the external temperature rises sharply, inflatable tents without pressure regulating valves may experience concentrated structural stress due to excessive air pressure, ultimately leading to airbag rupture or seam cracking.
Related Products
- Cell Phone:+86 15695147631
- Cell Phone:+86 18630605111
-
Email:
[email protected]
[email protected]
[email protected] - Add:No.9 Kangmin Road, Automobile industry Park, Yizheng City, Jiangsu Province, China
Copyright © Yangzhou Mailenda Outdoor Products Co., Ltd.
All Rights Reserved.
Custom Tent OEM/ODM Manufacturers

- Privacy Statement
- Terms & Conditions
- Sitemap


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 Español
Español 日本語
日本語 русский
русский عربى
عربى