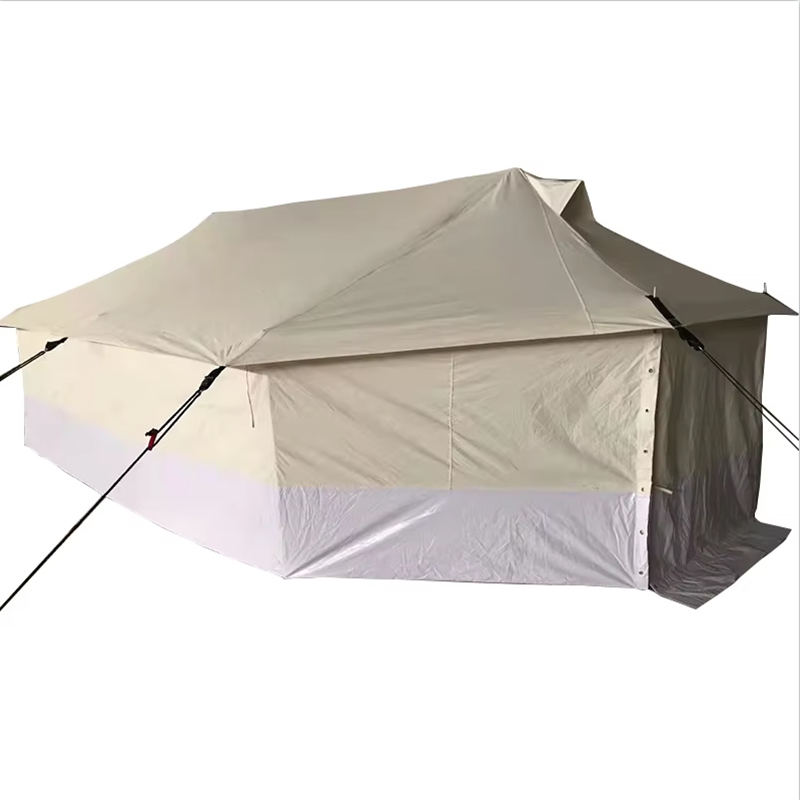
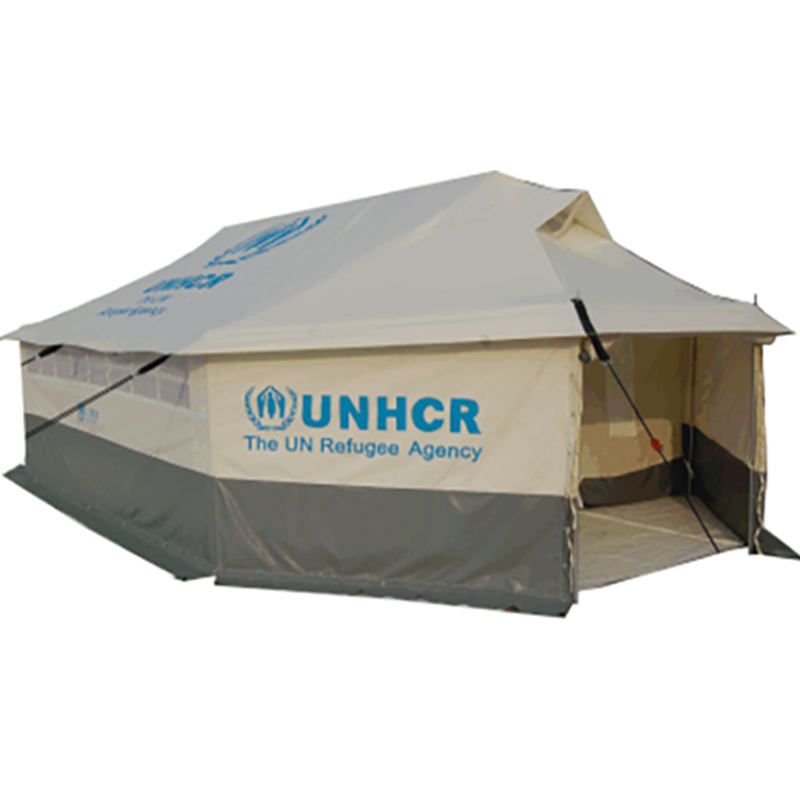
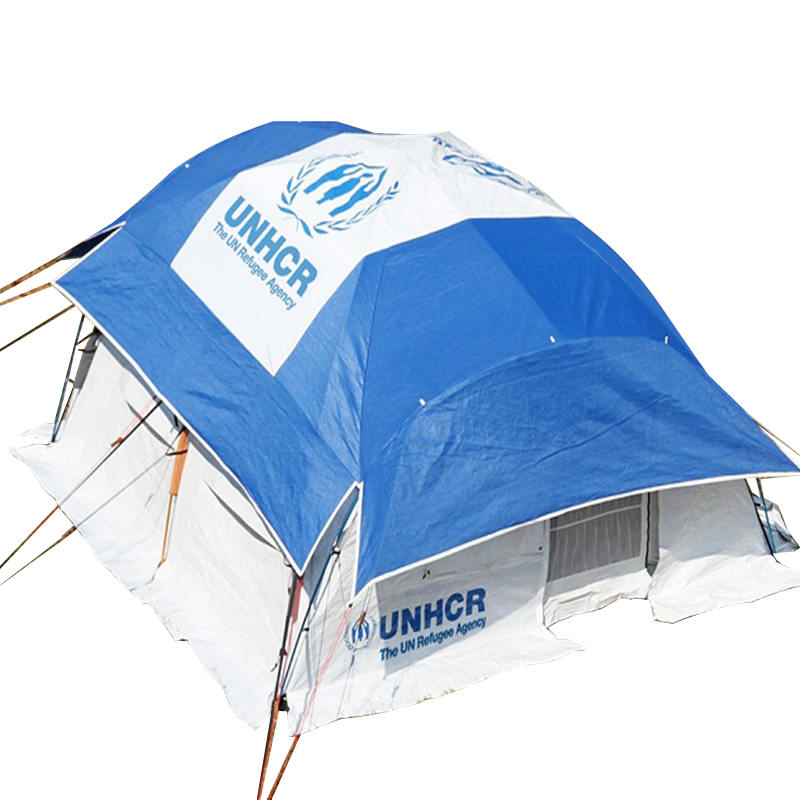
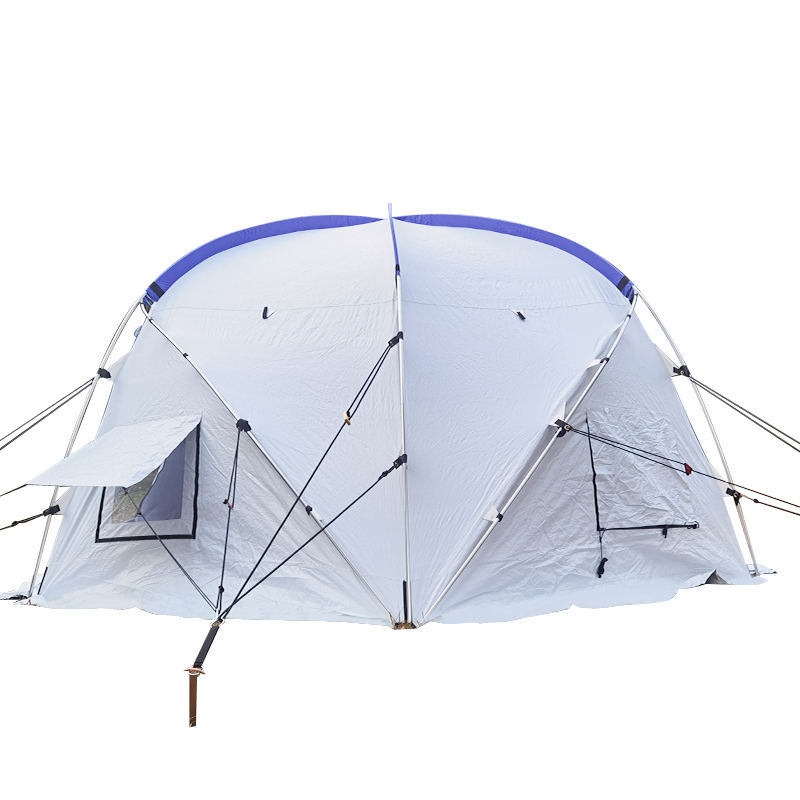
Our story is about how to uphold the spirit of humanitarianism in the face of disaster, how to find solutions amidst challenges, and how to sow hope in despair.
Web Menu
Product Search
Exit Menu
What materials help relief tent enhance windproof and waterproof performance?
Posted by Admin | 21 Nov
Content
- 1 What core fabrics lay the foundation for windproof and waterproof relief tent?
- 2 What coating technologies enhance the waterproof effect of relief tent?
- 3 What structural auxiliary materials improve the windproof stability of relief tent?
- 4 What functional materials optimize the comprehensive performance of relief tent in harsh environments?
What core fabrics lay the foundation for windproof and waterproof relief tent?
The windproof and waterproof performance of relief tent starts with the selection of core fabrics, which must withstand harsh natural conditions such as strong winds, heavy rains, and even hailstorms in disaster-stricken areas. High-strength polyester oxford cloth and nylon ripstop are the mainstream choices for relief tent fabrics—polyester oxford cloth has excellent tensile strength and wear resistance, which can resist the impact of strong winds without tearing, while the ripstop structure of nylon fabrics (reinforced with interwoven thick threads) prevents small cracks from expanding into large tears. These fabrics are woven with high-density warp and weft threads, reducing the gap between fibers and blocking rainwater penetration from the source. For extreme weather scenarios, some relief tent adopt composite fabrics with double-layer structures: the outer layer is a high-strength woven fabric for wind resistance, and the inner layer is a thin waterproof membrane for secondary protection. This fabric combination ensures that relief tent can maintain structural integrity and water tightness in severe weather, providing a safe shelter for disaster victims.
What coating technologies enhance the waterproof effect of relief tent?
Pure fabric materials are difficult to achieve absolute waterproofness, so professional coating technologies play a key role in enhancing the waterproof performance of relief tent. The most widely used coatings include polyurethane (PU) coating and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) coating. PU coating forms a uniform waterproof film on the fabric surface, which is lightweight and breathable while blocking rainwater, avoiding stuffiness inside the tent. PVC coating, on the other hand, has stronger waterproof and corrosion resistance, and can withstand long-term exposure to rainwater without degradation. Some high-performance relief tent adopt double-sided coating technology: the outer layer coating enhances water repellency, and the inner layer coating improves adhesion to the fabric, preventing the coating from peeling off during frequent use. In addition, the addition of fluorocarbon waterproof agents to the coating further enhances the water repellency—rainwater will form beads and slide off the tent surface without soaking the fabric. These coating technologies ensure that relief tent can effectively prevent rainwater penetration even in continuous heavy rain, keeping the interior dry.
What structural auxiliary materials improve the windproof stability of relief tent?
The windproof performance of relief tent not only depends on the fabric but also relies on structural auxiliary materials to enhance overall stability. High-strength aluminum alloy or fiberglass poles are the core support components of relief tent—aluminum alloy poles have high rigidity and fatigue resistance, which can withstand strong wind pressure without bending or breaking, while fiberglass poles are lightweight and flexible, adapting to wind direction changes to reduce the risk of breakage. The connection between the poles and the tent fabric uses reinforced webbing and high-strength sewing threads: the webbing distributes the wind force evenly to the entire tent body, avoiding local stress concentration, and the high-density stitching (with multiple stitches per centimeter) prevents the fabric from tearing at the seams. In addition, the ground anchor and wind rope system of relief tent are made of galvanized steel and high-strength polyester fiber: the ground anchor can be firmly inserted into the soil or fixed on hard ground, and the wind rope with adjustable tension can tighten the tent body, reducing wind resistance and preventing the tent from being blown over by strong winds. These structural auxiliary materials form a complete windproof system, ensuring that relief tent remains stable in gale conditions.
What functional materials optimize the comprehensive performance of relief tent in harsh environments?
In addition to core fabrics and structural materials, functional auxiliary materials further optimize the windproof and waterproof performance of relief tent, adapting to diverse harsh environments. For example, the tent seams are sealed with waterproof tape made of thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU), which melts and adheres to the stitching under high temperature, eliminating gaps that may cause water leakage. The zippers of relief tent are equipped with waterproof covers and rubber gaskets: the waterproof cover prevents rainwater from flowing into the tent through the zipper teeth, and the rubber gasket enhances the sealing between the zipper and the fabric. In cold and windy areas, some relief tent use thermal insulation and windproof liners made of hollow fiber materials—while maintaining warmth, the liner also reduces air circulation inside the tent, enhancing windproof effect. For coastal or humid disaster areas, the fabric and auxiliary materials of relief tent are treated with anti-mildew and anti-corrosion agents, preventing mold growth and material degradation caused by long-term humidity. These functional materials enable relief tent to adapt to different climate conditions, ensuring long-term reliability of windproof and waterproof performance in complex environments.
Related Products
- Cell Phone:+86 15695147631
- Cell Phone:+86 18630605111
-
Email:
[email protected]
[email protected]
[email protected] - Add:No.9 Kangmin Road, Automobile industry Park, Yizheng City, Jiangsu Province, China
Copyright © Yangzhou Mailenda Outdoor Products Co., Ltd.
All Rights Reserved.
Custom Tent OEM/ODM Manufacturers

- Privacy Statement
- Terms & Conditions
- Sitemap


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 Español
Español 日本語
日本語 русский
русский عربى
عربى