Our story is about how to uphold the spirit of humanitarianism in the face of disaster, how to find solutions amidst challenges, and how to sow hope in despair.
Web Menu
Product Search
Exit Menu
Greenhouse vs. Polytunnel: Which Growing Structure Is the Best Investment for Year-Round Yields?
Posted by Admin | 16 Feb
Content
For commercial growers and serious horticulturists, the decision to invest in a Greenhouse or a Polytunnel is a pivotal choice that dictates the operational success of a farm. While both structures aim to extend the growing season and protect crops from the elements, they utilize vastly different materials and thermal principles. Understanding the technical nuances of each is essential for maximizing ROI and ensuring crop health in unpredictable climates.
As global weather patterns become more volatile, growers frequently ask: "Which structure offers better wind resistance and heat retention?" The answer depends on your specific crop requirements and geographic location. From high-tech polycarbonate greenhouses to cost-effective industrial polytunnels, the right choice can increase annual productivity by over 40% by bypassing the limitations of traditional outdoor farming.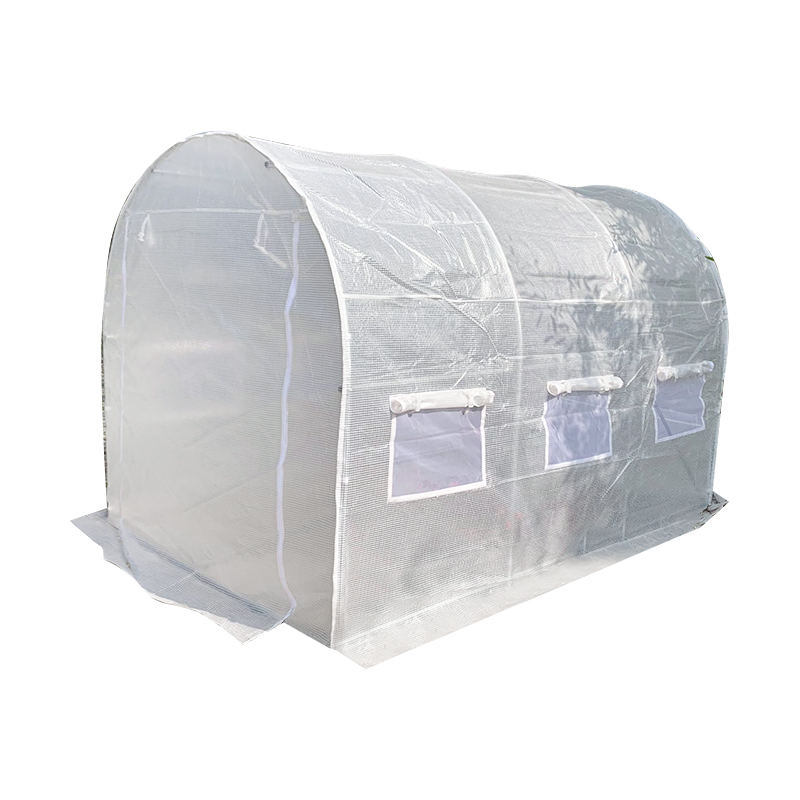
Technical Comparison: Structure, Insulation, and Durability
The primary difference lies in the cladding material and the frame architecture. Greenhouses typically use rigid glass or multi-wall polycarbonate panels, providing a permanent solution with high thermal mass. In contrast, polytunnels use high-density polyethylene (PE) or PVC films over galvanized steel hoops, offering a lightweight and modular approach to large-scale agriculture.
| Feature | Professional Greenhouse | Industrial Polytunnel |
|---|---|---|
| Cladding Material | Polycarbonate / Glass | UV-Stabilized PE Film |
| Heat Retention | Excellent (Multi-wall) | Moderate (Solar Gain) |
| Installation Complexity | High (Fixed Base Required) | Low (Rapid Deployment) |
| Cost per Square Meter | High (Premium Asset) | Low (Scalable Solution) |
For regions prone to heavy snowfall, the rigid frame of a greenhouse provides superior load-bearing capacity. However, in large-scale commercial berry or vegetable production, the polytunnel is often the preferred choice due to its ability to cover thousands of square meters at a fraction of the capital expenditure of a glasshouse.
Maximizing Crop Health with Advanced Climate Control
Enhanced UV Diffusion and Light Transmission
Modern polytunnels utilize "diffuse light" films that scatter incoming sunlight. This prevents "hot spots" and ensures that light reaches the lower leaves of the plants, promoting uniform growth. High-quality PE films now offer up to 90% light transmission, mimicking the clarity of glass while providing better protection against leaf scorch.
- Prevents fungal diseases by reducing internal condensation drip.
- Anti-dust additives keep the cover cleaner for longer, maintaining optimal light levels.
- Increases photosynthetic efficiency, leading to faster harvest cycles.
Strategic Ventilation and Pest Management
Both structures benefit from integrated side-roll ventilation. In a greenhouse, automated roof vents provide precise temperature regulation via PLC controllers. In polytunnels, full-length side curtains allow for massive airflow, which is critical for cooling crops during peak summer months. This natural ventilation significantly reduces the reliance on mechanical cooling, lowering electricity costs for the grower.
Economic Advantages and Long-Term Value
The economic return on a Greenhouse or Polytunnel is seen in the ability to market produce when supply is low. By harvesting tomatoes in late autumn or strawberries in early spring, growers can command premium prices that are often 200% higher than peak-season rates.
Key benefits for commercial agriculturalists include:
- Protection from soil-borne pests and airborne diseases, reducing chemical pesticide use.
- Water conservation through reduced evaporation and integrated rainwater harvesting from the structure’s roof.
- The ability to implement vertical growing systems to double or triple the yield per square meter.
Conclusion: Securing Your Agricultural Future
The transition from open-field farming to a Greenhouse or Polytunnel environment is the most effective way to future-proof an agricultural business. Whether you choose the structural permanence of a greenhouse or the scalable flexibility of a polytunnel, you are investing in climate resilience and consistent quality.
As consumer demand for high-quality, local produce grows, the ability to control every aspect of the growing environment becomes a major competitive advantage. By leveraging optimized light transmission and superior thermal protection, these structures allow growers to dominate their local markets regardless of the season. Investing in precision-engineered growing structures today ensures a stable, high-yield harvest for years to come, turning the challenges of the weather into a managed variable of success.
Related Products
- Cell Phone:+86 15695147631
- Cell Phone:+86 18630605111
-
Email:
[email protected]
[email protected]
[email protected] - Add:No.9 Kangmin Road, Automobile industry Park, Yizheng City, Jiangsu Province, China
Copyright © Yangzhou Mailenda Outdoor Products Co., Ltd.
All Rights Reserved.
Custom Tent OEM/ODM Manufacturers

- Privacy Statement
- Terms & Conditions
- Sitemap


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 Español
Español 日本語
日本語 русский
русский عربى
عربى